Contents
What is JSON?
- JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation
- JSON is lightweight text-data interchange format
- JSON is language independent *
- JSON is “self-describing” and easy to understand
*JSON uses JavaScript syntax for describing data objects, but JSON is still language and platform independent. JSON parsers and JSON libraries exists for many different programming languages.
Why JSON?
For AJAX applications, JSON is faster and easier than XML:
Using XML
- Fetch an XML document
- Use the XML DOM to loop through the document
- Extract values and store in variables
Using JSON
- Fetch a JSON string
- eval() the JSON string
Similar to XML
- JSON is plain text
- JSON is “self-describing” (human readable)
- JSON is hierarchical (values within values)
- JSON can be parsed by JavaScript
- JSON data can be transported using AJAX
Better than XML
- No end tag
- Shorter
- Quicker to read and write
- Can be parsed using built-in JavaScript eval()
- Uses arrays
- No reserved words
JSON Syntax
JSON syntax is a subset of JavaScript syntax
JSON syntax is a subset of the JavaScript object notation syntax.
- Data is in name/value pairs
- Data is separated by comma
- Curly brackets holds objects
- Square brackets holds arrays
JSON Name/Value Pairs
JSON data is written as name/value pairs.
A name/value pair consists of a field name (in double quotes), followed by a colon, followed by a value:
"firstName" : "John"JSON Values
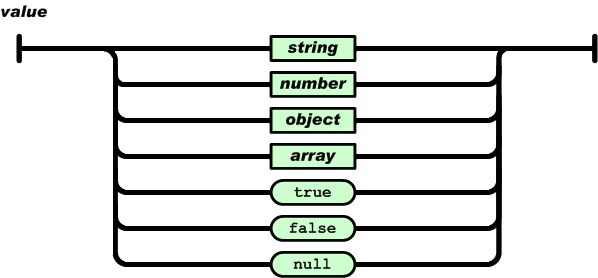
JSON values can be:
- A number (integer or floating point)
- A string (in double quotes)
- A Boolean (true or false)
- An array (in square brackets)
- An object (in curly brackets)
- null
JSON Objects
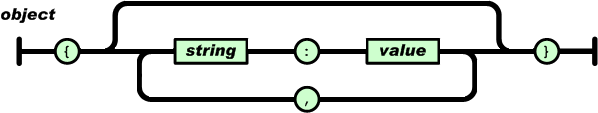
An object is an unordered set of name/value pairs. An object begins with { (left brace) and ends with } (right brace). Each name is followed by : (colon) and the name/value pairs are separated by , (comma).
JSON objects are written inside curly brackets,
Objects can contain multiple name/values pairs:
{ "firstName":"John" , "lastName":"Doe" }JSON Files
- The file type for JSON files is “.json”
- The MIME type for JSON text is “application/json”
JSON Video Tutorial for Beginners
[youtube http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wbB3lVyUvAM]Jquery JSON Systax
jQuery.getJSON( url, [ data ], [ success(data, textStatus, jqXHR) ] )
url – A string containing the URL to which the request is sent.
data – A map or string that is sent to the server with the request.
success(data, textStatus, jqXHR) – A callback function that is executed if the request succeeds.
Sample Jquery Code – json.js
$(document).ready(function(){
//attach a jQuery live event to the button
$('#getdata-button').live('click', function(){
$.getJSON('json.php', function(data) {
//alert(data); //uncomment this for debug
//alert (data.item1+" "+data.item2+" "+data.item3); //further debug
$('#showdata').html("<p>item1="+data.item1+" item2="+data.item2+" item3="+data.item3+"</p>");
});
});
});
Sample PHP Code – json.php
//request data from the database
//code here to connect to database and get the data you want
/* Example JSON format
{
"item1": "I love itzurkarthi.com",
"item2": "You love itzurkarthi.com",
"item3": "We love itzurkarthi.com"
}
*/
//return in JSON format
echo "{";
echo "item1: ", json_encode($item1), "\n";
echo "item2: ", json_encode($item2), "\n";
echo "item3: ", json_encode($item3), "\n";
echo "}";
HTML Code
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" " http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd ">
<html xmlns=" http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml ">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>Request json test</title>
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-1.5.js"></script>
<script src="json.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
</head>
<body>
<a href="#" id="getdata-button">Get JSON Data</a>
<div id="showdata"></div>
</body>
</html>
Please don’t forget to share and subscribe to latest updates of the blog. Also any comments and feedback are all welcome!
Thanks!
