Not too long ago, Google rolled out the “Speed Update,” considering the fact that people do not want to wait around for the answers they are searching for. Aimed at web pages delivering the slowest user experiences, it would only affect a small proportion of total search queries. Even then, Google understood the relationship between load time performance and how it affects the overall user experience.
Contents
But why should you care about it?
Load time is a big determining factor on whether a visitor to your website will stay or go. The longer the load time, or the amount of time it takes for a web page to show up on the screen, the more likely a visitor is to leave your website. In fact, if a web page takes longer than 3 seconds to load, 40% of visitors will leave.
And that is why load time is important, and it is all the more important to speed up your website. This article will show you the way.
Why Page Speed Matters
Page speed matters for two reasons: because having a slow load time increases your bounce rate which lowers conversions and because it is a ranking signal considered by Google.
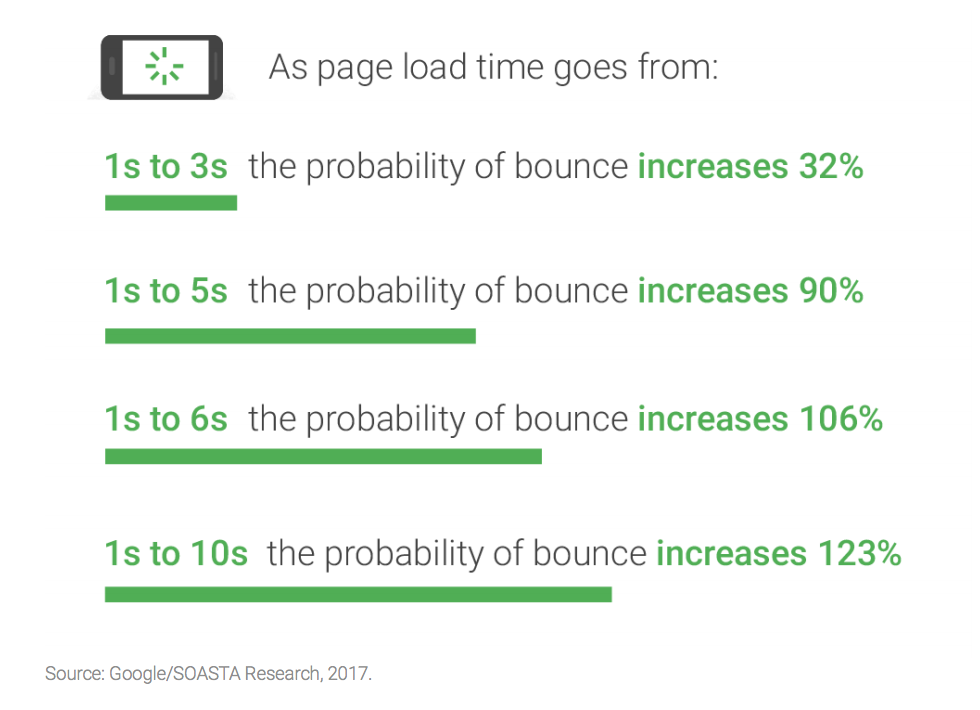
According to a Google study in 2017, they found that poor load times increase bounce rates.
As you can see, there is a tight correlation between load speed times and bounce rates. As load time increases, even by a few seconds, the bounce rates increase significantly. This research clearly shows what our intuition leads us to believe—that poor load times turn people away. Slow websites just aren’t attractive. Poor load times contribute greater bounce rate and considerably poorer sales, directly translating into a loss of revenue for you and your business. Speed is essential for that reason.
Google decided to consider it as a ranking factor because poor page speed load times create a poor user experience. Google is in the game of creating the best UX possible with their understanding that customers will remain loyal to a website that is quick, increasing their overall customer satisfaction. People just don’t want to wait, and Google has added that factor into its algorithm. You can think of having poor load times as a double hit—not only will you lower your conversion rate when users visit your website, you will also receive less traffic as a result of Google now considering it as an independent ranking signal.
Web page speed is a factor when determining the ranking of your website on Google’s search engine results. As you know, the higher your ranking, the greater success your website will have, and the more the better for you as a result.
Page speed refers to how fast the content on any given web page takes to fully load.
Faster web pages are just more efficient and create a better user experience. As it is, most people tend to have shorter attention spans, and when they want something, they want it now.
Page speed also affects conversions. For instance, Amazon conducted a theory and figured they would lose $1.6 billion every year if their website slowed down by a mere 1 second.
Overall, Google’s conclusion of web page load times as a ranking factor should be a huge factor in determining whether page speed really matters to your website.
Getting Started
Before discussing how to speed up a website, we should first understand the use of these 3 resources.. To get a deeper understanding of Google’s PageSpeed tools, visit their blog:
Chrome User Experience Report (CrUX)
CrUX is valuable resource filled with public data of key user experience metrics for popular websites on the Internet. According to Google, they looked to “capture the full range of external factors that shape and contribute to the final user experience,” with two separate focuses on “speed” and “optimization.”
Lighthouse
Lighthouse is an automated tool and works hand-in-hand with Chrome Developer Tools used in auditing the quality of web pages. The quality of web pages pertains to performance and accessibility among others.
PageSpeed Insights
PageSpeed Insights is a tool which entails how sufficiently a web page performs on Chrome’s UX (User Experience) Report. Additionally, it suggests performance optimizations.
How to Speed up Your Website
Minify
A tool cleaning up JavaScript and CSS code, it caches (a temporary process of storing data) them to optimize performance, thereby speeding up web page loads. It strips out unnecessary characters and spaces, reducing the overall file size and download time without changing functionality.
JavaScript is the most commonly used client side scripting language; it is the code written into an HTML (HyperText Markup Language—used to create web pages displayed on the Internet) web page. When JavaScript is involved on a web page, it sends the script to the browser. Thereafter, the browser determines what to do with it.
On the other hand, CSS code stands for Cascading Style Sheets. It is a series of instructions considered “statements,” which identify the elements of an HTML document and tells the web browser how to implement these elements.
Reduce Redirects
Because redirects often require extra processing time, it is important to serve your website to users directly. Redirects are a way of sending visitors and search engines from one URL to another. It makes it all the more confusing for the web browser, thereby inhibiting slow loading times.
To fix this, check any redirects and simplify them as much as possible using Google Page Speed Insights, which tells you any active redirects on your website.
Remove Render-blocking JavaScript
Parsing of JavaScript refers to analyzing or breaking down a code when converting one data type to another data type. This increases a web page load time as it keeps the web page from loading as quickly as it could.
In order to optimize your website, defer the parsing of unnecessary <script> tags. Google recommends you “avoid and minimize the use of blocking JavaScript” to improve loading time, as mentioned here.
To remove your render-blocking JavaScript, defer it by a script to call external JavaScript file, which should be placed in your website’s HTML just before the </body> tag (near the bottom of the HTML file).
Optimize Caching
There are content management systems like WordPress’s WP Super Cache plugin that will cache the latest version of your website’s pages. In turn, the browser will not be forced to dynamically generate that specific web page every single time for the user to see. For instance, the browser will save certain elements of a web page like images and JavaScript, or even the entire web page, so that next time it will not have to download it again.
By optimizing caching, you can take a huge chunk out of web page load times.
Improve Server Response Time
The amount of web traffic your website receives is a big factor on your server’s response time as well as the resources each web pages uses, the software your server uses, and the hosting solution you use.
To combat slow server response time, you must optimize your time to first byte (TTFB), which is a metric in determining how long your web browser takes to receive the first byte of a response from a web server when your request to visit a specific website. A byte is a unit of memory size.
You can optimize TTFB by caching your dynamic web pages, making them “pre-built” within the HTML so they are ready to go as soon as a web browser requests to visit the web pages. Plugins like WordPress’s Super Cache helps as well as server configuration, which is a common way to cache files yourself.
Use Content Delivery Network
Known as CDN, it works to reduce the web page load time. Amazon’s Cloudfront is a popular solution, as it provides access to a faster server near a user’s geographical location, thus speeding up loading time for your website. You can read more about how a CDN can speed up your load times on this post from 101domain’s blog.
Optimize Images
To ensure a fast loading time, optimize by resizing images on your website. High resolution images are heavy and because of this, take more bandwidth (the maximum data transfer rate of a network or Internet connection) and longer to process.
To fix this, use CSS sprites. These combine multiple images into one single image file, loading them all at one, resulting in fewer HTTP requests (HyperText Transfer Protocol—a portion of information one computer sends to communicate to another computer), and helping with performance. By doing this, you save load time and will not make users wait for several images to load at once.
There are some ways you can speed up your website.
Speeding up your website creates a better overall user experience. A better overall user experience makes for more repeat visits, more conversions, and more happy visitors. Happy visitors results in better search ranking for you and your website. What’s not to love?